

Testing report of Lamorite
Lamorite is the stone of CVD diamond mixed with Silicon Carbide, which adopting technical called Chemical Vapor Deposition(CVD) crystal formation, uniform carbon atoms deposition over surface of Silicon Carbide(Thickness 0.10-0.15μm (100-150nm), not only retaining the high refractive index and high thermal conductivity of Silicon Carbide, but also has the hardness of diamond, so it will never wear out ,like a diamond is forever.
Figure 1 is the optical micrograph of Lamorite, it shows the CVD diamond growing didn’t alter the optical properties of moissanite.

Figure 1 Optical Micrograpy. Left: Non-CVD ; Right: CVD
Figure 2 is the Scanning electron micrograph.High-magnification photographs (Fig. 2(a)) show uniform and dense diamond grains.Although the grains are very fine (50-100 nm), the typical facet characteristics of the diamond grains can still be clearly seen. The thickness of the diamond film is relatively uniform from the fracture photograph, which is between 100-150 nm.
(a) Low magnification photo showing the entire table area.
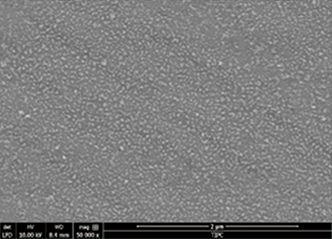
(b) High magnification photo showing finediamond grains with visible facet features.
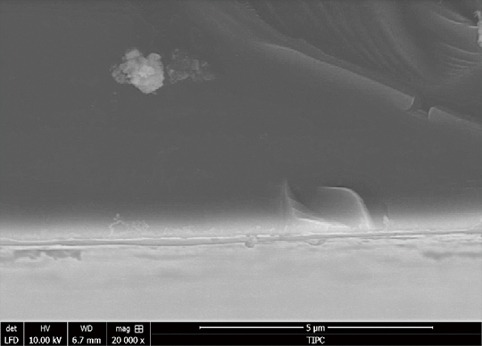
(c) Photograph of the fracture, the diamond is uniform and dense, and the thickness is about 100-150 nm.
Figure 3 shows a typical laser Raman spectrum of a Lamorite. A diamond characteristic peak located near 1338 cm-1 can be seen. The shift of the peak position relative to the standard peak position (1332.5 cm-1) indicates that there is a large stress in the diamond area. The Raman peak located near 1300 cm-1 is a nano diamond peak. The Raman peak near 1400 cm-1 is a typical non-diamond carbon peak. The lower peak intensity of the diamond is due to the small thickness of the diamond film.
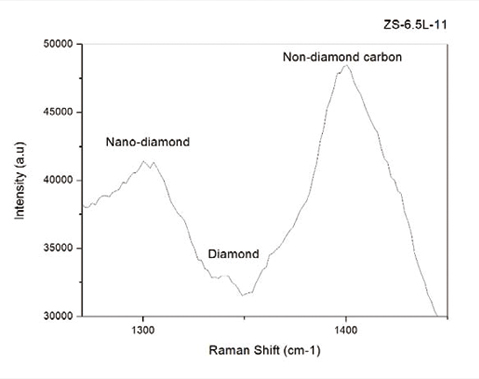
Figure 3 Typical laser Raman spectrum obtained from the surface of Lamorite.
The hardness of Lamorite which showing in figure 1 was tested by The HVT-1000 small-load Vickers hardness tester manufactured by Shanghai Lianer Testing Equipment Co., Ltd. A standard diamond indenter is used with a test load of 0.025 kg (0.245 N) and a dwell time of 10 seconds. Ten points were randomly tested. The length of the two diagonal lines of each indentation was measured by laser confocal microscope. The average value a was calculated by the formula: Hv=1854.4P/a2 to Vickers diamond hardness. The maximum Vickers hardness value obtained is 113.6GPa, and the minimum value is 69.9 GPa, with an average of 82.3 GPa ( Vickers hardness of natural diamond is 80-110 GPa). Figure 4 shows the typical Vickers hardness indentation morphology and diagonal length measurements under a laser confocal microscope. Note the crack at the top of the diagonal of the indentation because the diamond film and silicon carbide are both brittle materials.


Figure 4 Lamorite Vickers hardness indentation under laser confocal microscope (left), and indentation diagonal length measurement (right)

